The Role of Information and Contraceptive Use on Teen Pregnancy
Abstract
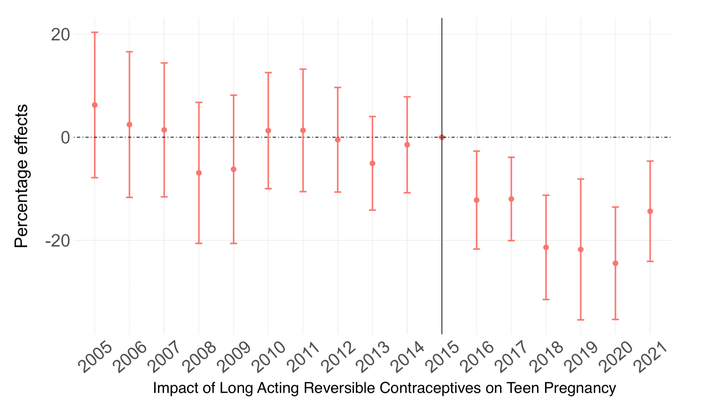
This paper investigates how information frictions affect the efficacy of contraception provision programs. We study a Costa-Rican initiative that aimed at reducing teenage pregnancies. The program combined free access to long-acting reversible contraceptives, eliciting baseline misperceptions about sexual health, and a tailored information campaign to correct for them. Exploiting the geographic variation in the initiative combined with administrative birth data, we find a 16% decrease in teen birth-rate. Using survey data on sexual behavior and beliefs, we show the policy changed the source of information from personal networks to healthcare professionals, which amends misinformation on sexual health and contraception use. The reduction in teen-birth is stronger in conservative districts, where restrictive social norms can explain teenagers’ lower knowledge about sexual health, contributing to risky behaviors.